
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Complications
- Risk of Depression according to Cumulative Exposure to a Low-Household Income Status in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population- Based Study
- So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Kyu-na Lee, Bongsung Kim, So Hyun Cho, So Yoon Kwon, Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Kyungdo Han, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):290-301. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0299
- 883 View
- 129 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
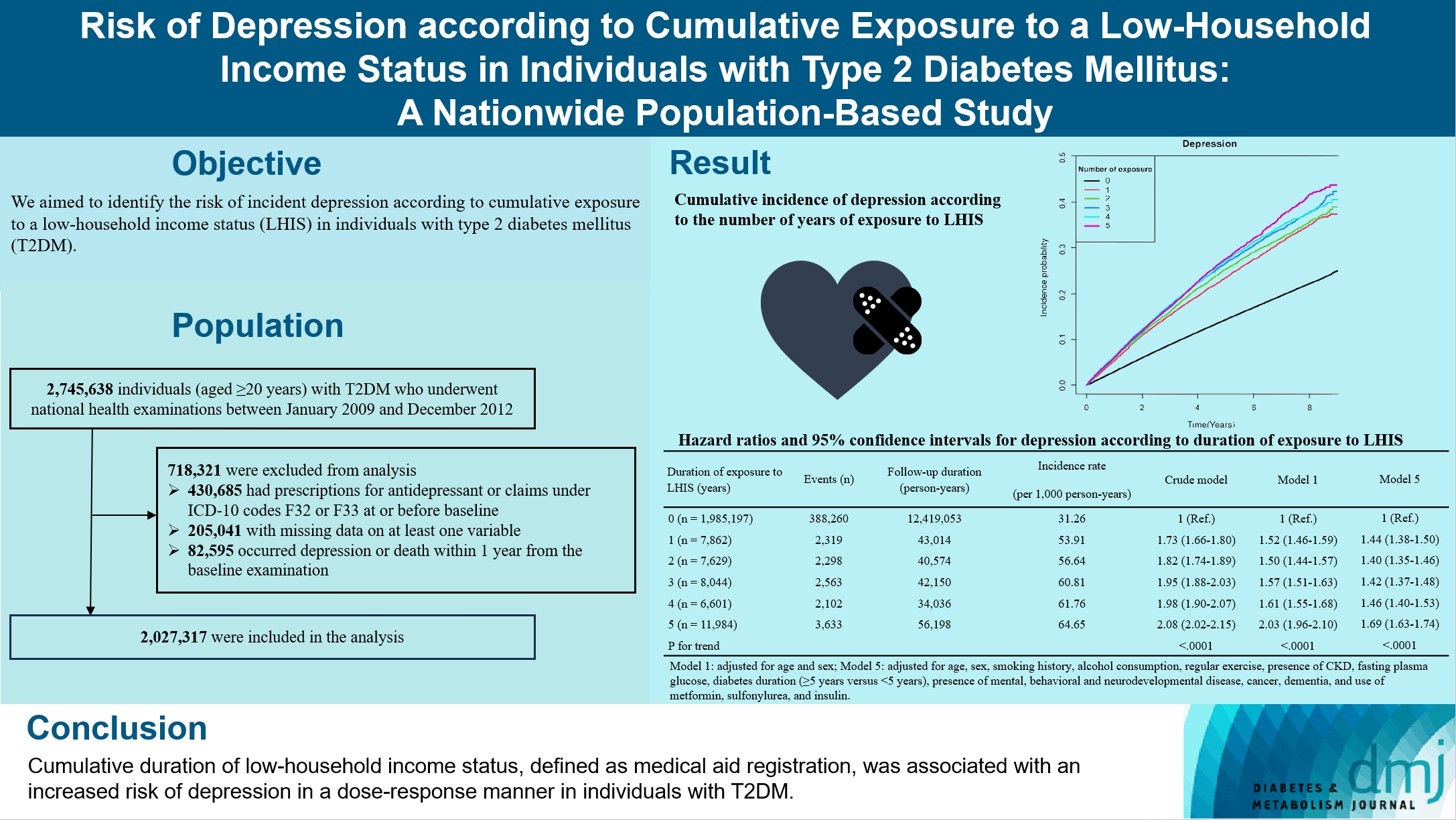
We aimed to identify the risk of incident depression according to cumulative exposure to a low-household income status in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
For this retrospective longitudinal population-based cohort study, we used Korean National Health Insurance Service data from 2002 to 2018. Risk of depression was assessed according to cumulative exposure to low-household income status (defined as Medical Aid registration) during the previous 5 years among adults (aged ≥20 years) with T2DM and without baseline depression who underwent health examinations from 2009 to 2012 (n=2,027,317).
Results
During an average 6.23 years of follow-up, 401,175 incident depression cases occurred. Advance in cumulative number of years registered for medical aid during the previous 5 years from baseline was associated with an increased risk of depression in a dose-dependent manner (hazard ratio [HR], 1.44 [95% confidence interval (CI), 1.38 to 1.50]; HR, 1.40 [95% CI, 1.35 to 1.46]; HR, 1.42, [95% CI, 1.37 to 1.48]; HR, 1.46, [95% CI, 1.40 to 1.53]; HR, 1.69, [95% CI, 1.63 to 1.74] in groups with 1 to 5 exposed years, respectively). Insulin users exposed for 5 years to a low-household income state had the highest risk of depression among groups categorized by insulin use and duration of low-household income status.
Conclusion
Cumulative duration of low-household income status, defined as medical aid registration, was associated with an increased risk of depression in a dose-response manner in individuals with T2DM.
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Low Household Income Status and Death from Pneumonia in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Study
- You-Bin Lee, So Hee Park, Kyu-na Lee, Bongsung Kim, So Yoon Kwon, Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Kyungdo Han, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):682-692. Published online June 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0184
- 1,584 View
- 121 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
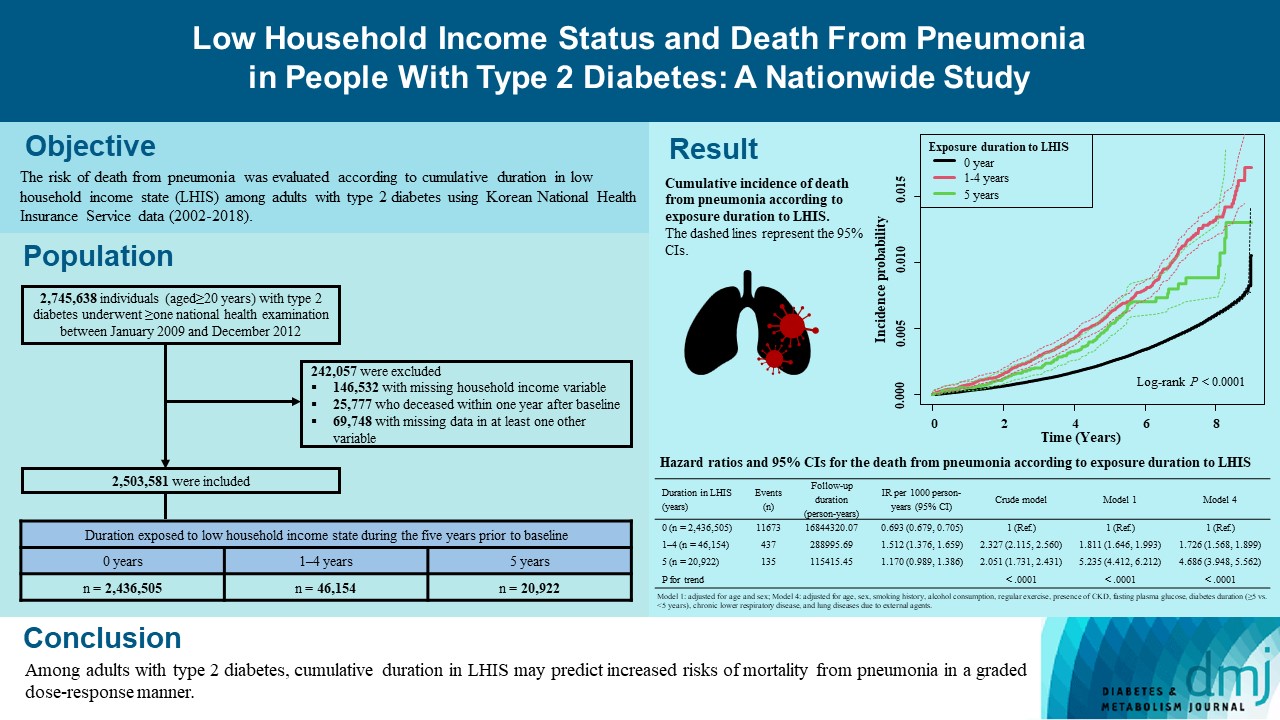
We explored the risk of death from pneumonia according to cumulative duration in low household income state (LHIS) among adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
Using Korean National Health Insurance Service data (2002 to 2018), the hazards of mortality from pneumonia were analyzed according to duration in LHIS (being registered to Medical Aid) during the 5 years before baseline (0, 1–4, and 5 years) among adults with T2DM who underwent health examinations between 2009 and 2012 (n=2,503,581). Hazards of outcomes were also compared in six groups categorized by insulin use and duration in LHIS.
Results
During a median 7.18 years, 12,245 deaths from pneumonia occurred. Individuals who had been exposed to LHIS had higher hazards of death from pneumonia in a dose-response manner (hazard ratio [HR], 1.726; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.568 to 1.899 and HR, 4.686; 95% CI, 3.948 to 5.562 in those exposed for 1–4 and 5 years, respectively) compared to the non-exposed reference. Insulin users exposed for 5 years to LHIS exhibited the highest outcome hazard among six groups categorized by insulin use and duration in LHIS.
Conclusion
Among adults with T2DM, cumulative duration in LHIS may predict increased risks of mortality from pneumonia in a graded dose-response manner. Insulin users with the longest duration in LHIS might be the group most vulnerable to death from pneumonia among adults with T2DM.
- Association of Body Mass Index and Fracture Risk Varied by Affected Bones in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:242-54)
- Se-Won Lee, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):439-440. Published online May 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0104
- [Original]
- 1,208 View
- 57 Download
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Two-Year Changes in Diabetic Kidney Disease Phenotype and the Risk of Heart Failure: A Nationwide Population-Based Study in Korea
- Seung Eun Lee, Juhwan Yoo, Han Seok Choi, Kyungdo Han, Kyoung-Ah Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):523-534. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0096
- 1,712 View
- 100 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
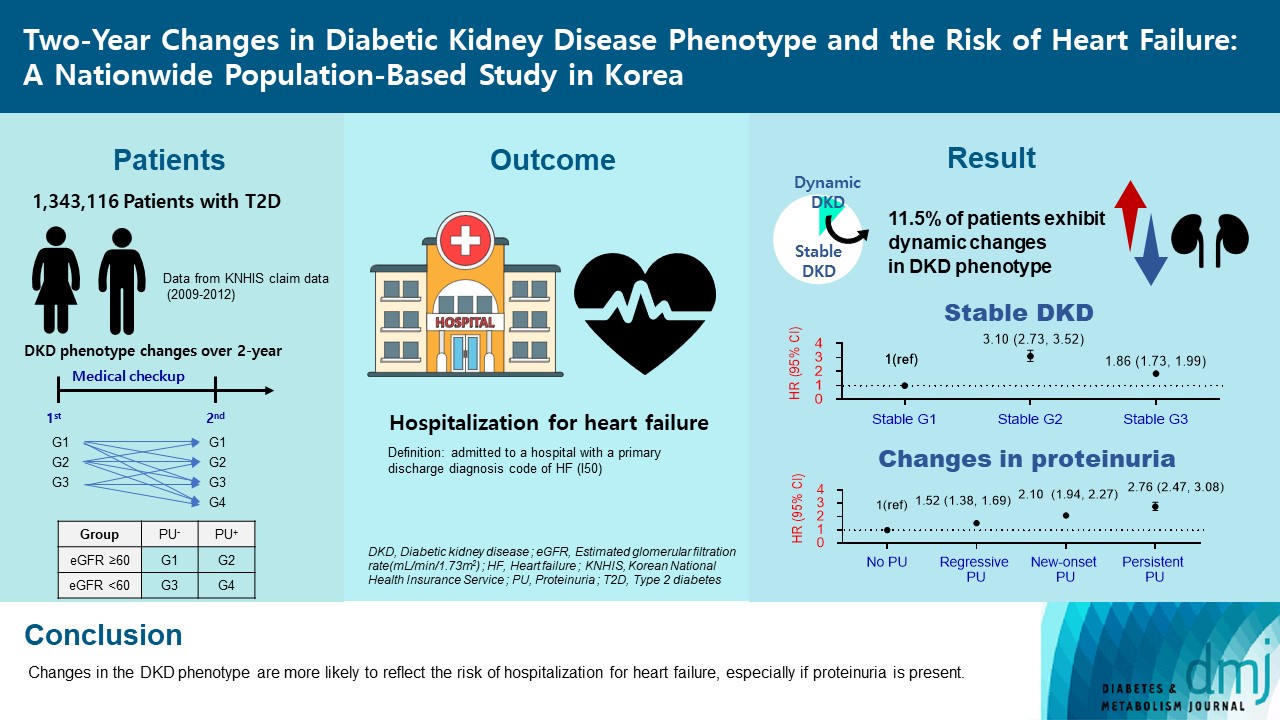
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a risk factor for hospitalization for heart failure (HHF). DKD could be classified into four phenotypes by estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR, normal vs. low) and proteinuria (PU, negative vs. positive). Also, the phenotype often changes dynamically. This study examined HHF risk according to the DKD phenotype changes across 2-year assessments.
Methods
The study included 1,343,116 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) from the Korean National Health Insurance Service database after excluding a very high-risk phenotype (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2) at baseline, who underwent two cycles of medical checkups between 2009 and 2014. From the baseline and 2-year eGFR and PU results, participants were divided into 10 DKD phenotypic change categories.
Results
During an average of 6.5 years of follow-up, 7,874 subjects developed HHF. The cumulative incidence of HHF from index date was highest in the eGFRlowPU– phenotype, followed by eGFRnorPU+ and eGFRnorPU–. Changes in DKD phenotype differently affect HHF risk. When the persistent eGFRnorPU– category was the reference, hazard ratios for HHF were 3.10 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.73 to 3.52) in persistent eGFRnorPU+ and 1.86 (95% CI, 1.73 to 1.99) in persistent eGFRlowPU–. Among altered phenotypes, the category converted to eGFRlowPU+ showed the highest risk. In the normal eGFR category at the second examination, those who converted from PU– to PU+ showed a higher risk of HHF than those who converted from PU+ to PU–.
Conclusion
Changes in DKD phenotype, particularly with the presence of PU, are more likely to reflect the risk of HHF, compared with DKD phenotype based on a single time point in patients with T2DM.
- Complications
- Association of Body Mass Index and Fracture Risk Varied by Affected Bones in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Cohort Study
- Se-Won Lee, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):242-254. Published online January 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0001
- 2,898 View
- 164 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
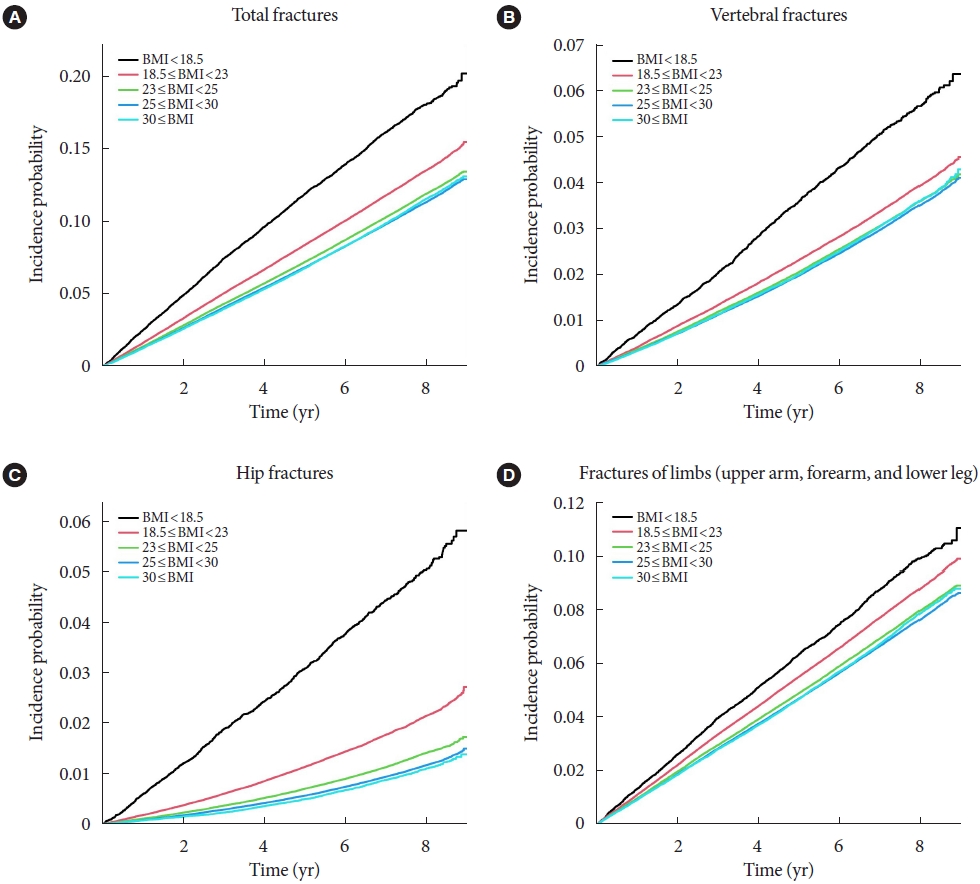
Body mass index (BMI) is a risk factor for the type 2 diabetes (T2DM), and T2DM accompanies various complications, such as fractures. We investigated the effects of BMI and T2DM on fracture risk and analyzed whether the association varied with fracture locations.
Methods
This study is a nationwide population-based cohort study that included all people with T2DM (n=2,746,078) who received the National Screening Program during 2009–2012. According to the anatomical location of the fracture, the incidence rate and hazard ratio (HR) were analyzed by dividing it into four categories: vertebra, hip, limbs, and total fracture.
Results
The total fracture had higher HR in the underweight group (HR, 1.268; 95% CI, 1.228 to 1.309) and lower HR in the obese group (HR, 0.891; 95% CI, 0.882 to 0.901) and the morbidly obese group (HR, 0.873; 95% CI, 0.857 to 0.89), compared to reference (normal BMI group). Similar trends were observed for HR of vertebra fracture. The risk of hip fracture was most prominent, the risk of hip fracture increased in the underweight group (HR, 1.896; 95% CI, 1.178 to 2.021) and decreased in the obesity (HR, 0.643; 95% CI, 0.624 to 0.663) and morbidly obesity group (HR, 0.627; 95% CI, 0.591 to 0.665). Lastly, fracture risk was least affected by BMI for limbs.
Conclusion
In T2DM patients, underweight tends to increase fracture risk, and overweight tends to lower fracture risk, but association between BMI and fracture risk varied depending on the affected bone lesions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dysuricemia—A New Concept Encompassing Hyperuricemia and Hypouricemia
Naoyuki Otani, Motoshi Ouchi, Einosuke Mizuta, Asuka Morita, Tomoe Fujita, Naohiko Anzai, Ichiro Hisatome
Biomedicines.2023; 11(5): 1255. CrossRef - Association of Body Mass Index and Fracture Risk Varied by Affected Bones in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:242-54)
Se-Won Lee, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 439. CrossRef - Association of Body Mass Index and Fracture Risk Varied by Affected Bones in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:242-54)
So Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 437. CrossRef - Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on fractures, BMD, and bone metabolism markers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Xin Wang, Fengyi Zhang, Yufeng Zhang, Jiayi Zhang, Yingli Sheng, Wenbo Wang, Yujie Li
Osteoporosis International.2023; 34(12): 2013. CrossRef
- Dysuricemia—A New Concept Encompassing Hyperuricemia and Hypouricemia
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Screening for Prediabetes and Diabetes in Korean Nonpregnant Adults: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2022
- Kyung Ae Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Suk Chon, Min Kyong Moon, on Behalf of the Committee of Clinical Practice Guideline of Korean Diabetes Association
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):819-826. Published online November 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0364

- 4,264 View
- 268 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Diabetes screening serves to identify individuals at high-risk for diabetes who have not yet developed symptoms and to diagnose diabetes at an early stage. Globally, the prevalence of diabetes is rapidly increasing. Furthermore, obesity and/or abdominal obesity, which are major risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), are progressively increasing, particularly among young adults. Many patients with T2DM are asymptomatic and can accompany various complications at the time of diagnosis, as well as chronic complications develop as the duration of diabetes increases. Thus, proper screening and early diagnosis are essential for diabetes care. Based on reports on the changing epidemiology of diabetes and obesity in Korea, as well as growing evidence from new national cohort studies on diabetes screening, the Korean Diabetes Association has updated its clinical practice recommendations regarding T2DM screening. Diabetes screening is now recommended in adults aged ≥35 years regardless of the presence of risk factors, and in all adults (aged ≥19) with any of the risk factors. Abdominal obesity based on waist circumference (men ≥90 cm, women ≥85 cm) was added to the list of risk factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oxidative Balance Score and New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Adults without Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study-Health Examinees (KoGES-HEXA) Cohort
Mid-Eum Moon, Dong Hyuk Jung, Seok-Jae Heo, Byoungjin Park, Yong Jae Lee
Antioxidants.2024; 13(1): 107. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Once-Weekly Semaglutide Versus Once-Daily Sitagliptin as Metformin Add-on in a Korean Population with Type 2 Diabetes
Byung-Wan Lee, Young Min Cho, Sin Gon Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Soo Lim, Amine Dahaoui, Jin Sook Jeong, Hyo Jin Lim, Jae Myung Yu
Diabetes Therapy.2024; 15(2): 547. CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index predicts type 2 diabetes mellitus more effectively than oral glucose tolerance test-derived insulin sensitivity and secretion markers
Min Jin Lee, Ji Hyun Bae, Ah Reum Khang, Dongwon Yi, Mi Sook Yun, Yang Ho Kang
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111640. CrossRef - Cumulative muscle strength and risk of diabetes: A prospective cohort study with mediation analysis
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Yan Liang, Wenji Chen, Duolao Wang, Zilin Sun, Bo Xie, Tongzhi Wu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 197: 110562. CrossRef - Revisiting the Diabetes Crisis in Korea: Call for Urgent Action
Jun Sung Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
Min Kyong Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 120. CrossRef
- Oxidative Balance Score and New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Adults without Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study-Health Examinees (KoGES-HEXA) Cohort
- Others
- Current Trends of Big Data Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
- Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):552-563. Published online July 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0193

- 5,718 View
- 277 Download
- 32 Web of Science
- 33 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Recently, medical research using big data has become very popular, and its value has become increasingly recognized. The Korean National Health Information Database (NHID) is representative of big data that combines information obtained from the National Health Insurance Service collected for claims and reimbursement of health care services and results obtained from general health examinations provided to all Korean adults. This database has several strengths and limitations. Given the large size, various laboratory data, and questionnaires obtained from medical check-ups, their longitudinal nature, and long-term accumulation of data since 2002, carefully designed studies may provide valuable information that is difficult to obtain from other forms of research. However, consideration of possible bias and careful interpretation when defining causal relationships is also important because the data were not collected for research purposes. After the NHID became publicly available, research and publications based on this database have increased explosively, especially in the field of diabetes and metabolism. This article reviews the history, structure, and characteristics of the Korean NHID. Recent trends in big data research using this database, commonly used operational diagnosis, and representative studies have been introduced. We expect further progress and expansion of big data research using the Korean NHID.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Weight change in patients with new‐onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with remission: Comprehensive real‐world data
Jinyoung Kim, Bongseong Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(2): 567. CrossRef - Repeated detection of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease increases the incidence risk of type 2 diabetes in young adults
Jin Hwa Kim, Young Sang Lyu, Mee Kyoung Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(1): 180. CrossRef - Diabetes severity and the risk of depression: A nationwide population-based study
Yunjung Cho, Bongsung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Affective Disorders.2024; 351: 694. CrossRef - Diabetes Duration, Cholesterol Levels, and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyu Na Lee, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Remnant cholesterol is an independent risk factor for the incidence of chronic kidney disease in newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A nationwide population-based study
Soo Yeon Jang, Minwoong Kang, Eyun Song, Ahreum Jang, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111639. CrossRef - Association of the Intensive Blood Pressure Target and Cardiovascular Outcomes in the Population With Chronic Kidney Disease: A Retrospective Study in Korea
Soo‐Young Yoon, Ji Yoon Kong, Su Jin Jeong, Jin Sug Kim, Hyeon Seok Hwang, Kyunghwan Jeong
Journal of the American Heart Association.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Depression according to Cumulative Exposure to a Low-Household Income Status in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population- Based Study
So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Kyu-na Lee, Bongsung Kim, So Hyun Cho, So Yoon Kwon, Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Kyungdo Han, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 290. CrossRef - Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 525. CrossRef - A nationwide cohort study on diabetes severity and risk of Parkinson disease
Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Seung Hwan Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
npj Parkinson's Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting the Risk of Insulin-Requiring Gestational Diabetes before Pregnancy: A Model Generated from a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea
Seung-Hwan Lee, Jin Yu, Kyungdo Han, Seung Woo Lee, Sang Youn You, Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon, Mee Kyoung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 129. CrossRef - Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 10. CrossRef - Comparison of Operational Definition of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Data from Korean National Health Insurance Service and Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jong Ha Baek, Yong-Moon Park, Kyung Do Han, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Han Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 201. CrossRef - Comorbidity Differences by Trajectory Groups as a Reference for Identifying Patients at Risk for Late Mortality in Childhood Cancer Survivors: Longitudinal National Cohort Study
Hyery Kim, Hae Reong Kim, Sung Han Kang, Kyung-Nam Koh, Ho Joon Im, Yu Rang Park
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2023; 9: e41203. CrossRef - Diabetes severity is strongly associated with the risk of active tuberculosis in people with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide cohort study with a 6-year follow-up
Ji Young Kang, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
Respiratory Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigation of the Relationship Between Psychiatry Visit and Suicide After Deliberate Self-harm: Longitudinal National Cohort Study
Hye Hyeon Kim, Chanyoung Ko, Ji Ae Park, In Han Song, Yu Rang Park
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2023; 9: e41261. CrossRef - Reply
Yeonghee Eun, Hyungjin Kim, Jaejoon Lee
Arthritis & Rheumatology.2023; 75(6): 1081. CrossRef - Fatty Liver & Diabetes Statistics in Korea: Nationwide Data 2009 to 2017
Eugene Han, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-ho Lee, Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Jung Hwan Park, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 347. CrossRef - Comparison of Cefepime with Piperacillin/Tazobactam Treatment in Patients with Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia
Bo-Guen Kim, Danbee Kang, Kyung Hoon Min, Juhee Cho, Kyeongman Jeon
Antibiotics.2023; 12(6): 984. CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to metabolic syndrome increases thyroid cancer risk in young adults: a population-based cohort study
Jinyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(4): 526. CrossRef - Risk of developing chronic kidney disease in young-onset Type 2 diabetes in Korea
Joonyub Lee, Seung-Hwan Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon, Jae Hyoung Cho, Kyungdo Han, Yeoree Yang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Affecting High Body Weight Variability
Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 163. CrossRef - Physical activity and reduced risk of fracture in thyroid cancer patients after thyroidectomy — a nationwide cohort study
Jinyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Jin-Hyung Jung, Jeonghoon Ha, Chaiho Jeong, Jun-Young Heu, Se-Won Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Yejee Lim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Ki-Ho Song, Ki-Hyun Baek
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of diabetes status on total and site-specific cancer risk in the elderly population: A nationwide cohort study
Kyuho Kim, Bongseong Kim, Hyunho Kim, Hyung Soon Park, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110866. CrossRef - Response to comments of Lai et al. “Proposal of one option for patient-centered, heterogeneous selection of antidiabetic drug”
Sunyoung Kim, Sang Youl Rhee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110864. CrossRef - Risk of Pancreatic Cancer and Use of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Propensity Score-Matching Analysis
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Soon Jib Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 426. CrossRef - Increased risk of ischemic stroke associated with elevated gamma-glutamyl transferase level in adult cancer survivors: a population-based cohort study
Kyuwoong Kim, Hyeyun Jung, Edvige Di Giovanna, Tae Joon Jun, Young-Hak Kim
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Real-world data analysis on effectiveness of integrative therapies: A practical guide to study design and data analysis using healthcare databases
Ye-Seul Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
Integrative Medicine Research.2023; 12(4): 101000. CrossRef - Possible Applications of the Korean Experience in the Development of Croatian Healthcare System
Predrag Bejakovic, Romina P Družeta, Ohmin Kwon
Science, Art and Religion.2023; 2(1--2): 26. CrossRef - Cumulative effect of impaired fasting glucose on the risk of dementia in middle-aged and elderly people: a nationwide cohort study
Jin Yu, Kyu-Na Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Alcohol consumption and the risk of liver disease: a nationwide, population-based study
Sang Yi Moon, Minkook Son, Yeo Wool Kang, Myeongseok Koh, Jong Yoon Lee, Yang Hyun Baek
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term Cumulative Exposure to High γ-Glutamyl Transferase Levels and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Han-Sang Baek, Bongseong Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Sang-Ah Chang, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 770. CrossRef - Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A nationwide propensity-score matched cohort study
Jinyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 194: 110187. CrossRef - Chronic viral hepatitis accelerates lung function decline in smokers
Suh-Young Lee, Sun-Sin Kim, So-Hee Lee, Heung-Woo Park
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2022; 23(6): 2159. CrossRef
- Weight change in patients with new‐onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with remission: Comprehensive real‐world data
- Others
- Fasting Glucose Variability and the Risk of Dementia in Individuals with Diabetes: A Nationwide Cohort Study
- Da Young Lee, Jaeyoung Kim, Sanghyun Park, So Young Park, Ji Hee Yu, Ji A Seo, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Sin Gon Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyungdo Han, Nan Hee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):923-935. Published online May 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0346
- 5,603 View
- 254 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We investigated whether fasting glucose (FG) variability could predict the risk of dementia.
Methods
This cohort study analyzed data from Koreans with diabetes after at least three health examinations by the Korean National Health Insurance Corporation between 2005 and 2010, which included at least one examination between 2009 and 2010. A total of 769,554 individuals were included, excluding those aged <40 years and those with dementia. FG variability was measured using the variability independent of the mean (FG-VIM). The incidence of dementia was defined by the International Classification of Diseases 10th Revision codes and prescription of anti-dementia medication and was subdivided into Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and vascular dementia (VD).
Results
During the 6.9-year follow-up, 54,837, 41,032, and 6,892 cases of all-cause dementia, AD, and VD, respectively, were identified. Cox proportional regression analyses showed that as the FG-VIM quartile increased, the risk of dementia serially increased after adjustment for metabolic factors, income status, and diabetes-related characteristics, including the mean FG. Participants in FG-VIM quartile 4 showed a 18%, 19%, and 17% higher risk for all-cause dementia, AD, and VD, respectively, than those in quartile 1; this particularly included non-obese patients with a longer duration of diabetes, high FG levels, dyslipidemia, and those taking glucose-lowering medications. Conversely, the baseline FG status and dementia showed a U-shaped association.
Conclusion
Increased FG variability over 5 years can predict the risk of dementia in individuals with diabetes in Korea. This finding was more pronounced in patients with less favorable metabolic profiles. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fasting glucose variability and risk of dementia in Parkinson’s disease: a 9-year longitudinal follow-up study of a nationwide cohort
Sung Hoon Kang, Yunjin Choi, Su Jin Chung, Seok-Joo Moon, Chi Kyung Kim, Ji Hyun Kim, Kyungmi Oh, Joon Shik Yoon, Sang Won Seo, Geum Joon Cho, Seong-Beom Koh
Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a Diabetic Microenvironment on Neurodegeneration: Special Focus on Neurological Cells
Vishal Chavda, Dhananjay Yadav, Snehal Patel, Minseok Song
Brain Sciences.2024; 14(3): 284. CrossRef - The Association of Glucose Variability and Dementia Incidence in Latinx Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Study
Heather Cuevas, Elizabeth Muñoz, Divya Nagireddy, Jeeyeon Kim, Grace Ganucheau, Fathia Alomoush
Clinical Nursing Research.2023; 32(2): 249. CrossRef - The effects of long-term cumulative HbA1c exposure on the development and onset time of dementia in the patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Hospital based retrospective study (2005–2021)
Sunyoung Cho, Choon Ok Kim, Bong-soo Cha, Eosu Kim, Chung Mo Nam, Min-Gul Kim, Min Soo Park
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 201: 110721. CrossRef - Physiological Mechanisms Inherent to Diabetes Involved in the Development of Dementia: Alzheimer’s Disease
Himan Mohamed-Mohamed, Victoria García-Morales, Encarnación María Sánchez Lara, Anabel González-Acedo, Teresa Pardo-Moreno, María Isabel Tovar-Gálvez, Lucía Melguizo-Rodríguez, Juan José Ramos-Rodríguez
Neurology International.2023; 15(4): 1253. CrossRef - Cumulative effect of impaired fasting glucose on the risk of dementia in middle-aged and elderly people: a nationwide cohort study
Jin Yu, Kyu-Na Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Fasting glucose variability and risk of dementia in Parkinson’s disease: a 9-year longitudinal follow-up study of a nationwide cohort
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Reproductive Life Span and Severe Hypoglycemia Risk in Postmenopausal Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Soyeon Kang, Yong-Moon Park, Dong Jin Kwon, Youn-Jee Chung, Jeong Namkung, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hyun Ko
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):578-591. Published online January 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0135
- 5,898 View
- 230 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
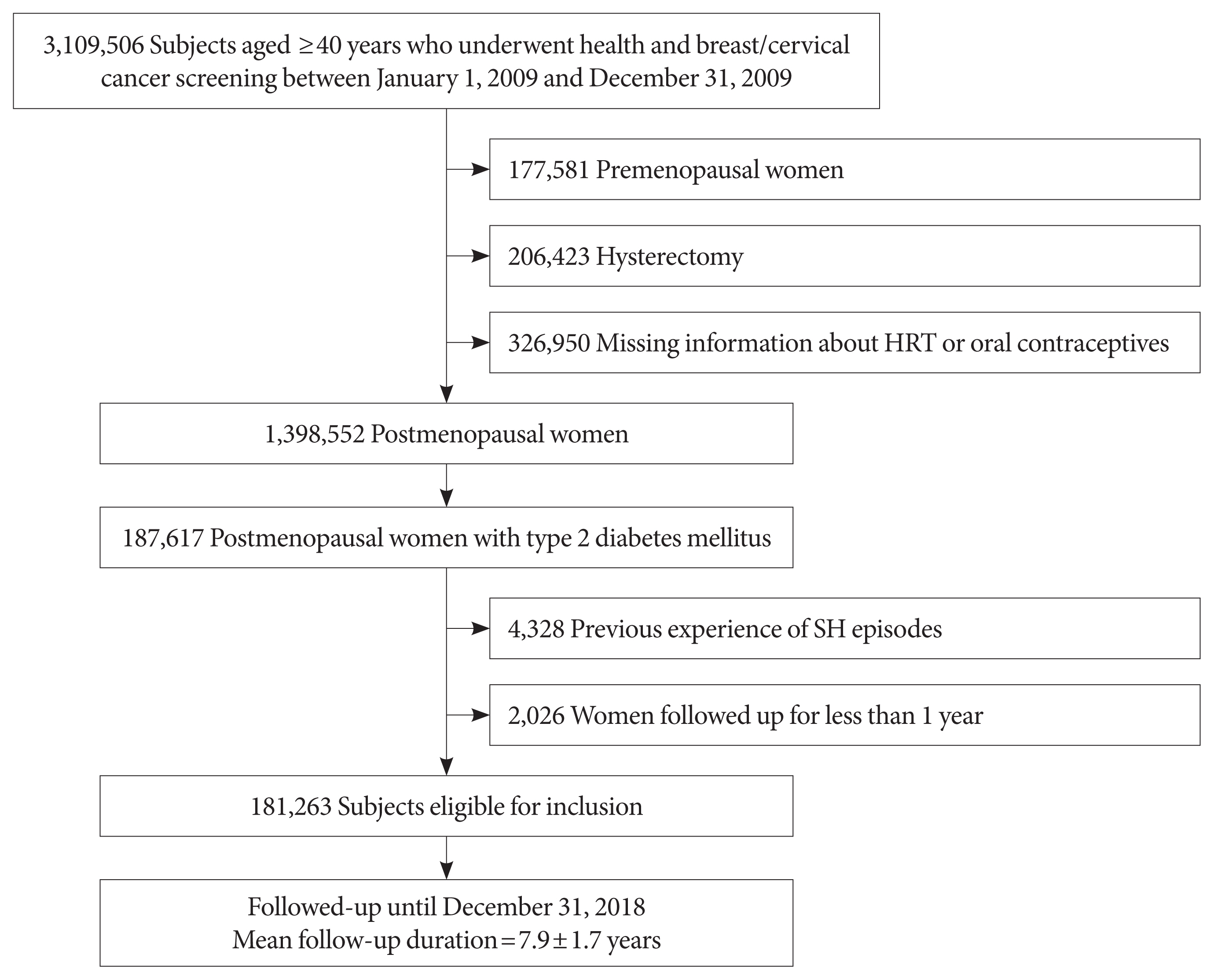
Estrogen promotes glucose homeostasis, enhances insulin sensitivity, and maintains counterregulatory responses in recurrent hypoglycemia in women of reproductive age. Postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) might be more vulnerable to severe hypoglycemia (SH) events. However, the relationship between reproductive factors and SH occurrence in T2DM remains unelucidated.
Methods
This study included data on 181,263 women with postmenopausal T2DM who participated in a national health screening program from January 1 to December 31, 2009, obtained using the Korean National Health Insurance System database. Outcome data were obtained until December 31, 2018. Associations between reproductive factors and SH incidence were assessed using Cox proportional hazards models.
Results
During the mean follow-up of 7.9 years, 11,279 (6.22%) postmenopausal women with T2DM experienced SH episodes. A longer reproductive life span (RLS) (≥40 years) was associated with a lower SH risk compared to a shorter RLS (<30 years) (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.74; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.69 to 0.80; P for trend <0.001) after multivariable adjustment. SH risk decreased with every 5-year increment of RLS (with <30 years as a reference [adjusted HR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.86 to 0.95; P=0.0001 for 30−34 years], [adjusted HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.76 to 0.84; P<0.001 for 35−39 years], [adjusted HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.68 to 0.81; P<0.001 for ≥40 years]). The use of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) was associated with a lower SH risk than HRT nonuse.
Conclusion
Extended exposure to endogenous ovarian hormone during lifetime may decrease the number of SH events in women with T2DM after menopause. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between serum copper level and reproductive health of Women in the United States: a cross-sectional study
Yi Yuan, Tong-Yu Peng, Guang-Yuan Yu, Zhao Zou, Meng-Ze Wu, Ruofei Zhu, Shuang Wu, Zi Lv, Su-Xin Luo
International Journal of Environmental Health Research.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Reproductive Lifespan and Motor Progression of Parkinson’s Disease
Ruwei Ou, Qianqian Wei, Yanbing Hou, Lingyu Zhang, Kuncheng Liu, Junyu Lin, Tianmi Yang, Jing Yang, Zheng Jiang, Wei Song, Bei Cao, Huifang Shang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(20): 6163. CrossRef - Menopause and development of Alzheimer’s disease: Roles of neural glucose metabolism and Wnt signaling
Paulina Villaseca, Pedro Cisternas, Nibaldo C. Inestrosa
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between serum copper level and reproductive health of Women in the United States: a cross-sectional study
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus among Korean Children, Adolescents, and Adults Younger than 30 Years: Changes from 2002 to 2016
- Yong Hee Hong, In-Hyuk Chung, Kyungdo Han, Sochung Chung, on Behalf of the Taskforce Team of the Obesity Fact Sheet of the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):297-306. Published online October 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0038
- 9,297 View
- 343 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
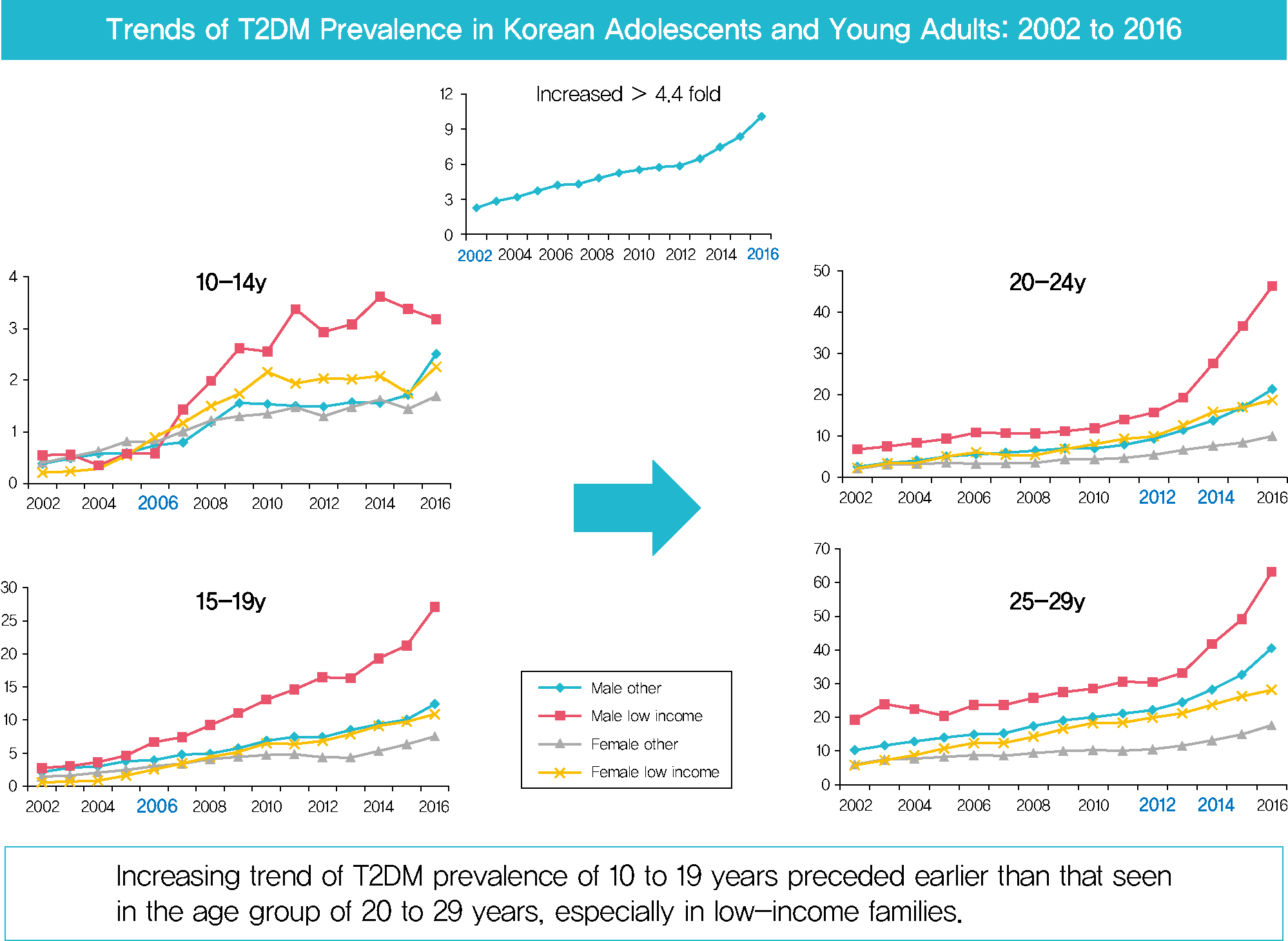
- Background
Despite the importance of and social concern regarding prevention of diabetes at younger ages, limited data are available. This study sought to analyze changes in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in Koreans younger than 30 years according to sex, age, and level of income.
Methods
The dataset analyzed in this study was derived from health insurance claims recorded in the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) database. Participants’ level of income was categorized as low (quintile 1, <20% of insurance premium) or others (quintile 2–5).
Results
In males and females, the prevalence of T2DM per 10,000 people steadily increased from 2.57 in 2002 to 11.41 in 2016, and from 1.96 in 2002 to 8.63 in 2016. The prevalence of T2DM in girls was higher in the age group of 5 to 14 years. Even though the prevalence was higher among those older than 20 years, the increase had started earlier, in the early 2000s, in younger age group. Adolescents aged 10 to 19 years in low-income families showed a remarkable increase in prevalence of T2DM, especially in boys.
Conclusion
The prevalence of T2DM in young Koreans increased more than 4.4-fold from 2002 to 2016, and the increase started in the early 2000s in younger age groups and in low-income families. This is the first study to examine the trend in prevalence of T2DM in children, adolescents, and young adults in Korea. Future studies and collaborations with social support systems to prevent T2DM at an early age group should be performed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- SCORE and SCORE2 in East Asian Population
JungMin Choi, Soseul Sung, Sue K. Park, Seyong Park, Hyoyeong Kim, Myeong-Chan Cho, Bryan Williams, Hae-Young Lee
JACC: Asia.2024; 4(4): 265. CrossRef - Chronic disease management program applied to type 2 diabetes patients and prevention of diabetic complications: a retrospective cohort study using nationwide data
Min Kyung Hyun, Jang Won Lee, Seung-Hyun Ko
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and pathological characteristics of DKD patients with early-onset type 2 diabetes
Liang Wu, Yi-Yang Zhao, Meng-Rui Li, Dong-Yuan Chang, Ming-Hui Zhao, Min Chen
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(8): 108520. CrossRef - Type 2 Diabetes and Its Association With Psychiatric Disorders in Young Adults in South Korea
Min-Kyung Lee, Su-Young Lee, Seo-Young Sohn, Jiyeon Ahn, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Hyuk Lee
JAMA Network Open.2023; 6(6): e2319132. CrossRef - Glycemic control and complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents during the COVID-19 outbreak
Kyeong Eun Oh, Yu Jin Kim, Ye Rim Oh, Eungu Kang, Hyo-Kyoung Nam, Young-Jun Rhie, Kee-Hyoung Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(4): 275. CrossRef - Position Statement on the Appropriateness and Significance of Adding the Glycated Hemoglobin Test to the National Health Examination
Ji Hye Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Jaehyun Kim, Sangjoon Park, Kyunghoon Lee, Jun Goo Kang, Eu Jeong Ku, Su Kyoung Kwon, Won Jun Kim, Young Sang Lyu, Jang Won Son, Young Sil Eom, Kyung Ae Lee, Jeongrim Lee, Jung Min Lee, Jung Hwa Lee, Jung Hwa Jung, Hochan Cho, Da
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 178. CrossRef - Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:880-9)
Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 349. CrossRef - Prevalence trends of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents in North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous federal state in Germany, 2002-2020
C. Baechle, A. Stahl-Pehe, N. Prinz, T. Meissner, C. Kamrath, R.W. Holl, J. Rosenbauer
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 190: 109995. CrossRef - Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Youth
Hwa Young Kim, Jae Hyun Kim
The Ewha Medical Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Affecting High-Risk for Diabetes among Korean Adolescents: An Analysis Using the Eighth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2020)
Kyung-Sook Bang, Sang-Youn Jang, Ji-Hye Choe
Children.2022; 9(8): 1249. CrossRef - Characteristics of Glycemic Control and Long-Term Complications in Patients with Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Han-sang Baek, Ji-Yeon Park, Jin Yu, Joonyub Lee, Yeoree Yang, Jeonghoon Ha, Seung Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Dong-Jun Lim, Hun-Sung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 641. CrossRef - 젊은 2형 당뇨병 환자의 관리
재현 배
Public Health Weekly Report.2022; 15(35): 2474. CrossRef
- SCORE and SCORE2 in East Asian Population
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Insulin Resistance Increases Serum Immunoglobulin E Sensitization in Premenopausal Women
- Seung Eun Lee, Ji Yeon Baek, Kyungdo Han, Eun Hee Koh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(2):175-182. Published online April 14, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0150
- 6,193 View
- 123 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
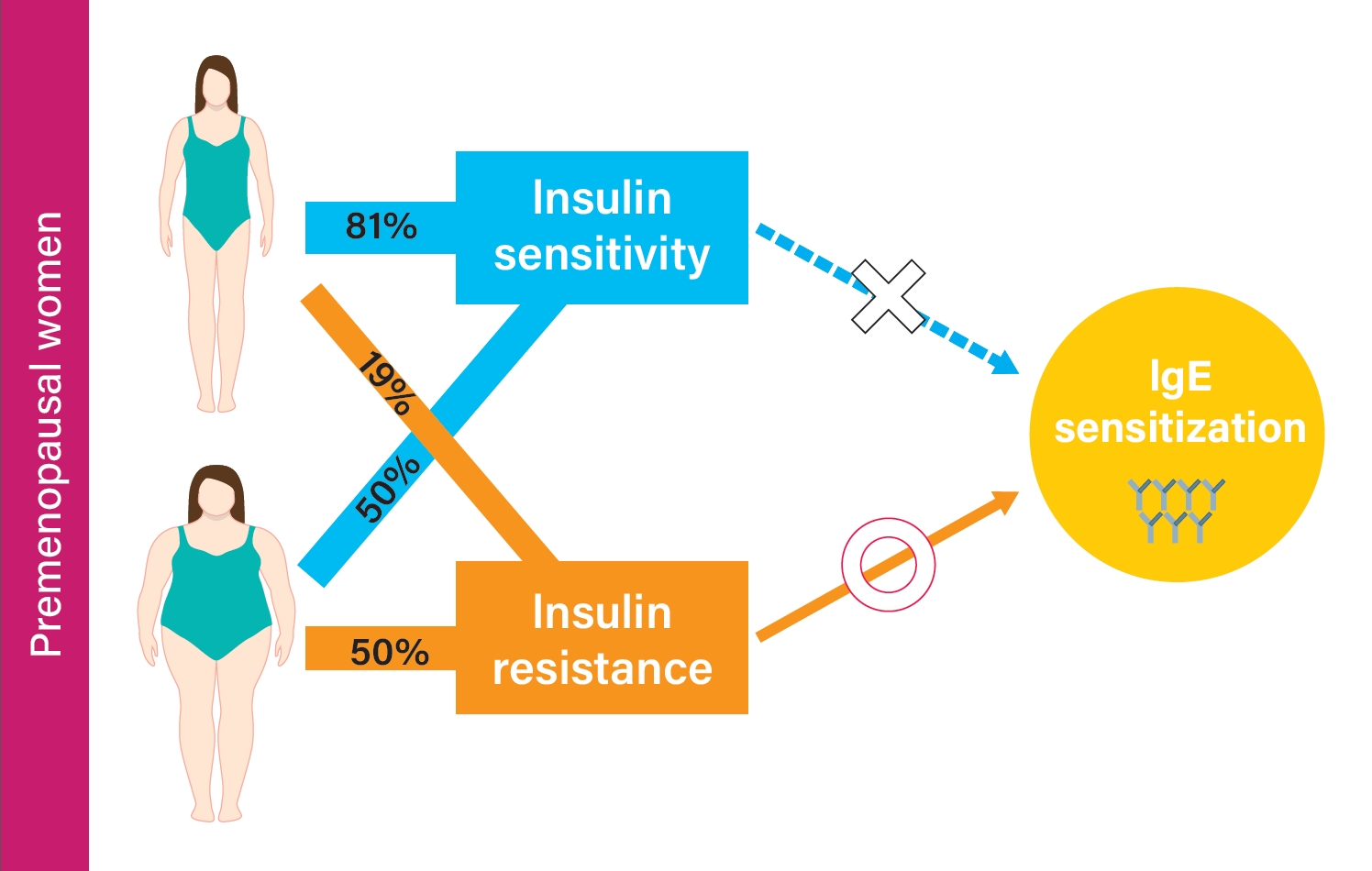
Background Although studies have shown that obesity is associated with aeroallergen sensitization (atopy), controversy still exists. We aimed to investigate the association between metabolic status, obesity, and atopy stratified by sex and menopausal status.
Methods A total of 1,700 adults from the 2010 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey were classified into metabolically healthy nonobese (MHNO), metabolically unhealthy nonobese (MUNO), metabolically healthy obese (MHO), and metabolically unhealthy obese (MUO) by body mass index and insulin resistance. Atopy was defined as a positive response to at least one aeroallergen. Multiple regression analysis was used to evaluate the risk of immunoglobulin E (IgE) elevation or atopy in relation to the degree of metabolic abnormality and obesity.
Results In premenopausal women, total IgE was positively correlated with obesity and insulin resistance. MUNO participants had a higher risk of having elevated total IgE compared to MHNO participants (odds ratio [OR], 2.271; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.201 to 4.294), while MHO participants did not show a significant difference (OR, 1.435; 95% CI, 0.656 to 3.137) in premenopausal women. MUNO, but not MHO was also associated with atopy (OR, 2.157; 95% CI, 1.284 to 3.625). In men and postmenopausal women, there was no significant difference between metabolic status, obesity, and atopy among groups.
Conclusion Increased insulin resistance is associated with total IgE and atopy in premenopausal women but not in postmenopausal women or men.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is There a Relationship between Insulin Resistance and Eosinophil, Inflammatory Parameters Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, C-Reactive Protein Values?
Meltem YİĞİT, Özgür OLUKMAN
Medical Records.2024; 6(1): 32. CrossRef
- Is There a Relationship between Insulin Resistance and Eosinophil, Inflammatory Parameters Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, C-Reactive Protein Values?
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Metabolic Health, Obesity, and the Risk of Developing Open-Angle Glaucoma: Metabolically Healthy Obese Patients versus Metabolically Unhealthy but Normal Weight Patients
- Younhea Jung, Kyungdo Han, Hae-Young L. Park, Seung Hoon Lee, Chan Kee Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):414-425. Published online December 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0048
- 6,812 View
- 122 Download
- 35 Web of Science
- 38 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background This study sought to investigate the associations between metabolic health status, obesity, and incidence of primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG).
Methods In this nationwide, population-based, longitudinal prospective cohort study conducted using the Korean National Health Insurance System, we categorized all subjects based on presence and severity of metabolic syndrome and obesity. Insurance claims data were used to identify POAG development. Then, Cox regression was applied to calculate the hazard of developing POAG in people with various components of metabolic syndrome, obesity, or their combination.
Results Of the total 287,553 subjects, 4,970 (1.3%) developed POAG. High fasting glucose, blood pressure, and total cholesterol levels were all associated with increased risk of developing POAG. Regarding obesity level, people with body mass index (BMI) greater than 30 kg/m2 were more likely to develop POAG than those with normal BMI. Also, people with greater number of metabolic syndrome components showed a greater POAG incidence. People who are metabolically unhealthy and obese (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 1.574; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.449 to 1.711) and those who are metabolically unhealthy nonobese (MUNO: adjusted HR, 1.521; 95% CI, 1.405 to 1.645) but not those who are metabolically healthy obese (MHO: adjusted HR, 1.019; 95% CI, 0.907 to 1.144) had an increased hazard of developing POAG compared with metabolically healthy nonobese (MHNO) subjects.
Conclusion Metabolic health status and obesity were significantly associated with increased risk of POAG incidence. MUNO subjects but not MHO subjects showed a higher risk of POAG development than did MHNO subjects, suggesting that metabolic status is more important than obesity in POAG.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Association between the Gut Microbiota and Erectile Dysfunction
Tianle Zhu, Xi Liu, Peng Yang, Yukuai Ma, Pan Gao, Jingjing Gao, Hui Jiang, Xiansheng Zhang
The World Journal of Men's Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Potentially compromised systemic and local lactate metabolic balance in glaucoma, which could increase retinal glucose and glutamate concentrations
Mina Arai-Okuda, Yusuke Murai, Hidetaka Maeda, Akiyasu Kanamori, Takako Miki, Tomoko Naito, Kazunobu Sugihara, Michihiro Kono, Masaki Tanito, Hiromitsu Onoe, Kazuyuki Hirooka, Yoshiaki Kiuchi, Masakazu Shinohara, Sentaro Kusuhara, Sotaro Mori, Kaori Ueda,
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and the Risk of Glaucoma in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes
Siar Niazi, Filip Gnesin, Anna-Sophie Thein, Jens R. Andreasen, Anna Horwitz, Zaynab A. Mouhammad, Baker N. Jawad, Zia Niazi, Nelsan Pourhadi, Bochra Zareini, Amani Meaidi, Christian Torp-Pedersen, Miriam Kolko
Ophthalmology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Glycemic Traits and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Mendelian Randomization Study in the Japanese Population
Akiko Hanyuda, Atsushi Goto, Masahiro Nakatochi, Yoichi Sutoh, Akira Narita, Shiori Nakano, Ryoko Katagiri, Kenji Wakai, Naoyuki Takashima, Teruhide Koyama, Kokichi Arisawa, Issei Imoto, Yukihide Momozawa, Kozo Tanno, Atsushi Shimizu, Atsushi Hozawa, Keng
American Journal of Ophthalmology.2023; 245: 193. CrossRef - Microbiome Dysbiosis: A Pathological Mechanism at the Intersection of Obesity and Glaucoma
Salvatore Pezzino, Maria Sofia, Luigi Piero Greco, Giorgia Litrico, Giulia Filippello, Iacopo Sarvà, Gaetano La Greca, Saverio Latteri
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(2): 1166. CrossRef - Phenotypic and Genetic Links between Body Fat Measurements and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
Shi Song Rong, Xinting Yu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3925. CrossRef - Metabolic Health, Obesity, and Intraocular Pressure
Younhea Jung, Gyoung Nyun Kim, Eun Byeol Oh, Kyoung Ohn, Jung Il Moon
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(5): 2066. CrossRef - Association between lifestyle habits and glaucoma incidence: a retrospective cohort study
Asahi Fujita, Yohei Hashimoto, Hiroki Matsui, Hideo Yasunaga, Makoto Aihara
Eye.2023; 37(16): 3470. CrossRef - Towards precision medicine in bariatric surgery prescription
Sofia S. Pereira, Marta Guimarães, Mariana P. Monteiro
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2023; 24(5): 961. CrossRef - Study of the relationship between serum lipid levels and primary open-angle glaucoma
Rajesh Subhash Joshi, Vaishnavi Hitesh Adatiya
Indian Journal of Ophthalmology.2023; 71(5): 1948. CrossRef - Primary open-angle glaucoma risk prediction with ABCA1 and LOC102723944 variants and their genotype–phenotype correlations in southern Chinese population
Zhenggen Wu, Chukai Huang, Yuqian Zheng, Xiang-Ling Yuan, Shaowan Chen, Yanxuan Xu, Li Jia Chen, Chi Pui Pang, Mingzhi Zhang, Tsz Kin Ng
Molecular Genetics and Genomics.2023; 298(6): 1343. CrossRef - Differences in Factors Associated With Glaucoma Progression With Lower Normal Intraocular Pressure in Superior and Inferior Halves of the Optic Nerve Head
Ryo Asaoka, Rei Sakata, Takeshi Yoshitomi, Aiko Iwase, Chota Matsumoto, Tomomi Higashide, Motohiro Shirakashi, Makoto Aihara, Kazuhisa Sugiyama, Makoto Araie
Translational Vision Science & Technology.2023; 12(8): 19. CrossRef - The association between obesity and glaucoma in older adults: evidence from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
Xiaohuan Zhao, Qiyu Bo, Junran Sun, Jieqiong Chen, Tong Li, Xiaoxu Huang, Minwen Zhou, Jing Wang, Wenjia Liu, Xiaodong Sun
Epidemiology and Health.2023; 45: e2023034. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome as an independent risk factor for glaucoma: a nationally representative study
Jun-Hyuk Lee, Yu-Jin Kwon, Sung Jin Kim, Boyoung Joung
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors: Interaction Issues in Patients with Glaucoma and Arterial Hypertension. Review
S. I. Makogon, D. I. Ivanova, A. L. Onishchenko
Ophthalmology in Russia.2023; 20(4): 641. CrossRef - The role of the microbiota in glaucoma
Ling Huang, Yiwen Hong, Xiangyu Fu, Haishan Tan, Yongjiang Chen, Yujiao Wang, Danian Chen
Molecular Aspects of Medicine.2023; 94: 101221. CrossRef - Girl Power in Glaucoma: The Role of Estrogen in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma
Kyrylo Fotesko, Bo Schneider Vohra Thomsen, Miriam Kolko, Rupali Vohra
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology.2022; 42(1): 41. CrossRef - Cholesterol and glaucoma: a systematic review and meta‐analysis
Laura Posch‐Pertl, Monja Michelitsch, Gernot Wagner, Brigitte Wildner, Günther Silbernagel, Gudrun Pregartner, Andreas Wedrich
Acta Ophthalmologica.2022; 100(2): 148. CrossRef - Non-drug interventions in glaucoma: Putative roles for lifestyle, diet and nutritional supplements
Foroogh Fahmideh, Nicoletta Marchesi, Annalisa Barbieri, Stefano Govoni, Alessia Pascale
Survey of Ophthalmology.2022; 67(3): 675. CrossRef - Relationship between Using Fibrate and Open-Angle Glaucoma in Hyperlipidemic Patients: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Yung-En Tsai, Yi-Hao Chen, Chien-An Sun, Chi-Hsiang Chung, Wu-Chien Chien, Ke-Hung Chien
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(4): 2415. CrossRef - The Causal Association Between Obesity and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
Yi Lin, Xiaomin Zhu, Wangdu Luo, Bingcai Jiang, Qianyi Lin, Min Tang, Xiangji Li, Lin Xie
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Enzymatic activity of paraoxonase depending on polymorphism Q192R of the PON1 gene in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma
Yu.E. Filippova, T.N. Malishevskaya, S.A. Petrov, D.G. Gubin, A.S. Vlasova
Vestnik oftal'mologii.2022; 138(2): 58. CrossRef - Association of Metabolic Syndrome With Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension in a Midwest United States Population
Kristi Y. Wu, David O. Hodge, Launia J. White, Jacinta McDonald, Gavin W. Roddy
Journal of Glaucoma.2022; 31(6): e18. CrossRef - Metabolically Defined Body Size Phenotypes and Risk of Endometrial Cancer in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC)
Nathalie Kliemann, Romain Ould Ammar, Carine Biessy, Audrey Gicquiau, Verena Katzke, Rudolf Kaaks, Anne Tjønneland, Anja Olsen, Maria-Jose Sánchez, Marta Crous-Bou, Fabrizio Pasanisi, Sandar Tin Tin, Aurora Perez-Cornago, Dagfinn Aune, Sofia Christakoudi,
Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.2022; 31(7): 1359. CrossRef - Clinical Practice Management of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma in the United States: An Analysis of Real-World Evidence
Joseph S Imperato, Kelly H Zou, Jim Z Li, Tarek A Hassan
Patient Preference and Adherence.2022; Volume 16: 2213. CrossRef - Meta-Analysis of Dyslipidemia and Blood Lipid Parameters on the Risk of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
Guimei Huang, Jiayi Wang, Lei Li, Yuan Gao, Yijie Yan, Xi Lou
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Body shape and risk of glaucoma: A Mendelian randomization
Ruolan Yuan, Kangcheng Liu, Yingjun Cai, Fei He, Xiaoxiong Xiao, Jing Zou
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Systemic Comorbidities on Ocular Hypertension and Open-Angle Glaucoma, in a Population from Spain and Portugal
Carolina Garcia-Villanueva, Elena Milla, José M. Bolarin, José J. García-Medina, Javier Cruz-Espinosa, Javier Benítez-del-Castillo, José Salgado-Borges, Francisco J. Hernández-Martínez, Elena Bendala-Tufanisco, Irene Andrés-Blasco, Alex Gallego-Martinez,
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(19): 5649. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome and its components are associated with non-arteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy
Darrell Kohli, Kristi Y Wu, Launia J White, David O Hodge, John J Chen, Gavin W Roddy
BMJ Open Ophthalmology.2022; 7(1): e001111. CrossRef - Blood Pressure Measures and Incident Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
Carmelo Macri, Christopher X. Wong, Samuel J. Tu, Robert Casson, Kuldev Singh, Sophia Y. Wang, Michelle T. Sun
Investigative Opthalmology & Visual Science.2022; 63(13): 3. CrossRef - Relationship between anthropometric and biochemical changes of metabolic syndrome with retinal nerve fiber layer and macular thickness
Sze Hui New, Sue Ngein Leow, Suresh Kumar Vasudevan, Idayu Badilla Idris, Seng Fai Tang, Norshamsiah Md Din, Bang V Bui
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(2): e0246830. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome and the aging retina
Gavin W. Roddy
Current Opinion in Ophthalmology.2021; 32(3): 280. CrossRef - Automated Detection of Glaucoma With Interpretable Machine Learning Using Clinical Data and Multimodal Retinal Images
Parmita Mehta, Christine A. Petersen, Joanne C. Wen, Michael R. Banitt, Philip P. Chen, Karine D. Bojikian, Catherine Egan, Su-In Lee, Magdalena Balazinska, Aaron Y. Lee, Ariel Rokem
American Journal of Ophthalmology.2021; 231: 154. CrossRef - Association of Hypertriglyceridemia and Incident Glaucoma in a Rural Chinese Population: The Handan Eye Study
Ye Zhang, Qing Zhang, Ravi Thomas, Si Zhen Li, Ning Li Wang
Translational Vision Science & Technology.2021; 10(8): 25. CrossRef - Risk of Glaucoma Associated with Components of Metabolic Disease in Taiwan: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Ya-Wen Chang, Fung-Chang Sung, Ya-Ling Tzeng, Chih-Hsin Mou, Peng-Tai Tien, Cheng-Wen Su, Yu-Kuei Teng
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 19(1): 305. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome Is Associated With Ocular Hypertension and Glaucoma
Gavin W. Roddy
Journal of Glaucoma.2020; 29(9): 726. CrossRef - Association of dipping status of blood pressure, visual field defects, and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in patients with normotensive glaucoma
Seung Uk Lee, Han Su Park, Bong Joon Kim, Hyun Su Kim, Jung Ho Heo, Sung Il Im
Medicine.2020; 99(50): e23565. CrossRef - Ocular findings in metabolic syndrome: a review
Mário Lima-Fontes, Pedro Barata, Manuel Falcão, Ângela Carneiro
Porto Biomedical Journal.2020; 5(6): 104. CrossRef
- The Association between the Gut Microbiota and Erectile Dysfunction
- Clinical Complications
- Incidence and Risk Factors for Dementia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population-Based Study in Korea
- Ji Hee Yu, Kyungdo Han, Sanghyun Park, Hanna Cho, Da Young Lee, Jin-Wook Kim, Ji A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Yong Gyu Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seon Mee Kim, Nan Hee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):113-124. Published online November 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0216
- 7,847 View
- 197 Download
- 31 Web of Science
- 32 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Diabetes mellitus is associated with an increased risk of dementia. We aimed to comprehensively analyze the incidence and risk factors for dementia and young-onset dementia (YOD) in diabetic patients in Korea using the National Health Insurance Service data.
Methods Between January 1, 2009 and December 31, 2012, a total of 1,917,702 participants with diabetes were included and followed until the date of dementia diagnosis or until December 31, 2015. We evaluated the incidence and risk factors for all dementia, Alzheimer's disease (AD), and vascular dementia (VaD) by Cox proportional hazards analyses. We also compared the impact of risk factors on the occurrence of YOD and late-onset dementia (LOD).
Results During an average of 5.1 years of follow-up, the incidence of all types of dementia, AD, or VaD was 9.5, 6.8, and 1.3/1,000 person-years, respectively, in participants with diabetes. YOD comprised 4.8% of all dementia occurrence, and the ratio of AD/VaD was 2.1 for YOD compared with 5.5 for LOD. Current smokers and subjects with lower income, plasma glucose levels, body mass index (BMI), and subjects with hypertension, dyslipidemia, vascular complications, depression, and insulin treatment developed dementia more frequently. Vascular risk factors such as smoking, hypertension, and previous cardiovascular diseases were more strongly associated with the development of VaD than AD. Low BMI and a history of stroke or depression had a stronger influence on the development of YOD than LOD.
Conclusion The optimal management of modifiable risk factors may be important for preventing dementia in subjects with diabetes mellitus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unlocking the Protective Potential of Upper Respiratory Infection Treatment Histories against Alzheimer’s Disease: A Korean Adult Population Study
Ho Suk Kang, Ji Hee Kim, Joo-Hee Kim, Woo Jin Bang, Hyo Geun Choi, Nan Young Kim, Ha Young Park, Mi Jung Kwon
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(1): 260. CrossRef - Hepatopancreatic metabolic disorders and their implications in the development of Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia
Francisco I. Pinheiro, Irami Araújo-Filho, Amália C.M. do Rego, Eduardo P. de Azevedo, Ricardo N. Cobucci, Fausto P. Guzen
Ageing Research Reviews.2024; 96: 102250. CrossRef - Amygdala activity and amygdala-hippocampus connectivity: Metabolic diseases, dementia, and neuropsychiatric issues
Juhyun Song
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 162: 114647. CrossRef - The effects of long-term cumulative HbA1c exposure on the development and onset time of dementia in the patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Hospital based retrospective study (2005–2021)
Sunyoung Cho, Choon Ok Kim, Bong-soo Cha, Eosu Kim, Chung Mo Nam, Min-Gul Kim, Min Soo Park
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 201: 110721. CrossRef - Association of triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with severe complications of COVID-19
Yoonkyung Chang, Jimin Jeon, Tae-Jin Song, Jinkwon Kim
Heliyon.2023; 9(6): e17428. CrossRef - Akkermansia muciniphila in neuropsychiatric disorders: friend or foe?
Wenhui Lei, Yiwen Cheng, Jie Gao, Xia Liu, Li Shao, Qingming Kong, Nengneng Zheng, Zongxin Ling, Weiming Hu
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association Between Eye Disease and Incidence of Dementia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jiayi Feng, Cuihong Huang, Lei Liang, Chuang Li, Xiaojie Wang, Jianping Ma, Xinhui Guan, Bin Jiang, Shaofen Huang, Pei Qin
Journal of the American Medical Directors Association.2023; 24(9): 1363. CrossRef - Risk of Neurodegenerative Diseases in Elderly Koreans with an Initial Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Retrospective Cohort Study
Hee-Cheol Kim, Ho-Jun Lee, Yang-Tae Kim, Byeong-Churl Jang, Asirvatham Alwin Robert
Journal of Diabetes Research.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Type-2 Diabetes Alters Hippocampal Neural Oscillations and Disrupts Synchrony between the Hippocampus and Cortex
Gratianne Rabiller, Zachary Ip, Shahram Zarrabian, Hongxia Zhang, Yoshimichi Sato, Azadeh Yazdan-Shahmorad, Jialing Liu
Aging and disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sarcopenia and diabetes-induced dementia risk
Mingyang Sun, Zhongyuan Lu, Wan-Ming Chen, Szu-Yuan Wu, Jiaqiang Zhang
Brain Communications.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of periodontitis with microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus: A nationwide cohort study
Moo-Seok Park, Jimin Jeon, Tae-Jin Song, Jinkwon Kim
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2022; 36(2): 108107. CrossRef - Association between oral health and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with hypertension: a nationwide cohort study
Jinkwon Kim, Hyung Jun Kim, Jimin Jeon, Tae-Jin Song
Journal of Hypertension.2022; 40(2): 374. CrossRef - Diabetic retinopathy and cognitive dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Mei Wu, Fan Mei, Kaiyan Hu, Liyuan Feng, Zhe Wang, Qianqian Gao, Fei Chen, Li Zhao, Xiaohui Li, Bin Ma
Acta Diabetologica.2022; 59(4): 443. CrossRef - Associations between depression and cognition, mild cognitive impairment and dementia in persons with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Yeng Yan Chow, Milou Verdonschot, Claire T. McEvoy, Geeske Peeters
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 185: 109227. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus: A Path to Amnesia, Personality, and Behavior Change
Rahnuma Ahmad, Kona Chowdhury, Santosh Kumar, Mohammed Irfan, Govindool Reddy, Farhana Akter, Dilshad Jahan, Mainul Haque
Biology.2022; 11(3): 382. CrossRef - Hypothyroidism and Diabetes-Related Dementia: Focused on Neuronal Dysfunction, Insulin Resistance, and Dyslipidemia
Hee Kyung Kim, Juhyun Song
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(6): 2982. CrossRef - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus as a Risk Factor for Alzheimer’s Disease: Review and Meta-Analysis
Athanasia Athanasaki, Konstantinos Melanis, Ioanna Tsantzali, Maria Ioanna Stefanou, Sofia Ntymenou, Sotirios G. Paraskevas, Theodosis Kalamatianos, Eleni Boutati, Vaia Lambadiari, Konstantinos I. Voumvourakis, George Stranjalis, Sotirios Giannopoulos, Ge
Biomedicines.2022; 10(4): 778. CrossRef - Cardiometabolic measures and cognition in early menopause - Analysis of baseline data from a randomized controlled trial
Lubna Pal, Kelly Morgan, Nanette F. Santoro, JoAnn E. Manson, Hugh S. Taylor, Virginia M. Miller, Eliot A. Brinton, Rogerio Lobo, Genevieve Neal-Perry, Marcelle I. Cedars, S. Mitchell Harman, Taryn T. James, Carey E. Gleason
Maturitas.2022; 162: 58. CrossRef - Dysfunctional Glucose Metabolism in Alzheimer’s Disease Onset and Potential Pharmacological Interventions
Vijay Kumar, So-Hyeon Kim, Kausik Bishayee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(17): 9540. CrossRef - Metabolically healthy obesity: it is time to consider its dynamic changes
Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(4): 123. CrossRef - Association between cholesterol levels and dementia risk according to the presence of diabetes and statin use: a nationwide cohort study
You-Bin Lee, Min Young Kim, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim, Sang-Man Jin
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The insulin resistance by triglyceride glucose index and risk for dementia: population-based study
Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Alzheimer's Research & Therapy.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The identification of established modifiable mid-life risk factors for cardiovascular disease which contribute to cognitive decline: Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging (KLoSA)
Yebeen Ysabelle Boo, Otto-Emil Jutila, Meghan A. Cupp, Logan Manikam, Sung-Il Cho
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research.2021; 33(9): 2573. CrossRef - Examining the effects of multiple chronic conditions on cognitive decline and potential moderators among older Koreans: Findings from the Korean Longitudinal Study of Ageing 2006–2016
Yura Lee, Chi C. Cho
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2021; 95: 104424. CrossRef - Cumulative Exposure to Metabolic Syndrome Components and the Risk of Dementia: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Yunjung Cho, Kyungdo Han, Da Hye Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Kun-Ho Yoon, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(2): 424. CrossRef - Cardiovascular risks of periodontitis and oral hygiene indicators in patients with diabetes mellitus
Tae-Jin Song, Jimin Jeon, Jinkwon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism.2021; 47(6): 101252. CrossRef - Association Between Diabetic Retinopathy and Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Dihe Cheng, Xue Zhao, Shuo Yang, Guixia Wang, Guang Ning
Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Improving Cognition with Nutraceuticals Targeting TGF-β1 Signaling
Margherita Grasso, Giuseppe Caruso, Justyna Godos, Angela Bonaccorso, Claudia Carbone, Sabrina Castellano, Walter Currenti, Giuseppe Grosso, Teresa Musumeci, Filippo Caraci
Antioxidants.2021; 10(7): 1075. CrossRef - The risk of Alzheimer’s disease according to dynamic changes in metabolic health and obesity: a nationwide population-based cohort study
Yun Kyung Cho, Jiwoo Lee, Hwi Seung Kim, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee, Ye-Jee Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Aging.2021; 13(13): 16974. CrossRef - Letter: Hypoglycemia and Dementia Risk in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Propensity-Score Matched Analysis of a Population-Based Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:125–33)
Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(2): 356. CrossRef - The Interplay between Diabetes and Alzheimer’s Disease—In the Hunt for Biomarkers
Adriana Kubis-Kubiak, Aleksandra Dyba, Agnieszka Piwowar
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(8): 2744. CrossRef - Association between cytomegalovirus end-organ diseases and moderate-to-severe dementia: a population-based cohort study
Kyoung Hwa Lee, Da Eun Kwon, Kyung Do Han, Yeonju La, Sang Hoon Han
BMC Neurology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Unlocking the Protective Potential of Upper Respiratory Infection Treatment Histories against Alzheimer’s Disease: A Korean Adult Population Study
- Epidemiology
- Associations between Breastfeeding and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Glycemic Control in Parous Women: A Nationwide, Population-Based Study
- Ga Eun Nam, Kyungdo Han, Do-Hoon Kim, Youn Huh, Byoungduck Han, Sung Jung Cho, Yong Gyu Park, Yong-Moon Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(2):236-241. Published online December 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0044
- 4,034 View
- 45 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader We investigated associations between breastfeeding duration and number of children breastfed and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and glycemic control among parous women. We performed a cross-sectional analysis of data for 9,960 parous women from the Korea National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey (2010 to 2013). Having ever breastfed was inversely associated with prevalent T2DM (adjusted odds ratio [OR], 0.60; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.42 to 0.87). All ranges of total and average breastfeeding duration showed inverse associations with T2DM. Even short periods of breastfeeding were inversely associated with T2DM (adjusted OR, 0.61; 95% CI, 0.38 to 0.99 for a total breastfeeding duration ≤12 months; adjusted OR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.42 to 0.99 for an average breastfeeding duration per child ≤6 months). A longer duration of breastfeeding was associated with better glycemic control in parous women with T2DM (
P trend=0.004 for total breastfeeding duration;P trend <0.001 for average breastfeeding duration per child). Breastfeeding may be associated with a lower risk of T2DM and good glycemic control in parous women with T2DM. Breastfeeding may be a feasible method to prevent T2DM and improve glycemic control.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Integration of nutrigenomics, melatonin, serotonin and inflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of pregnancy-specific urinary incontinence in women with gestational diabetes mellitus
Danielle Cristina Honorio França, Eduardo Luzía França, Luis Sobrevia, Angélica Mércia Pascon Barbosa, Adenilda Cristina Honorio-França, Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2023; 1869(6): 166737. CrossRef - Association of lactation with maternal risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of observational studies
Ana‐Catarina Pinho‐Gomes, Georgia Morelli, Alexandra Jones, Mark Woodward
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(8): 1902. CrossRef - Updates in Gestational Diabetes Prevalence, Treatment, and Health Policy
Laura T. Dickens, Celeste C. Thomas
Current Diabetes Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Integration of nutrigenomics, melatonin, serotonin and inflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of pregnancy-specific urinary incontinence in women with gestational diabetes mellitus
- Epidemiology
-
- High Proportion of Adult Cases and Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Population in Korea: A Nationwide Study
- You-Bin Lee, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Seung-Eun Lee, Ji Eun Jun, Jiyeon Ahn, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(1):76-89. Published online August 22, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0048
- 5,860 View
- 109 Download
- 26 Web of Science
- 30 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background The prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) in all age groups and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with T1DM in Korea were estimated.
Methods The incidence and prevalence of T1DM between 2007 and 2013 were calculated using the Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) datasets of claims. Clinical characteristics and prevalence of metabolic syndrome in individuals with T1DM between 2009 and 2013 were determined using the database of NHIS preventive health checkups.
Results The prevalence of T1DM in Korea between 2007 and 2013 was 0.041% to 0.047%. The annual incidence rate of T1DM in Korea in 2007 to 2013 was 2.73 to 5.02/100,000 people. Although the incidence rate of typical T1DM was highest in teenagers, it remained steady in adults over 30 years of age. In contrast, the incidence rate of atypical T1DM in 2013 was higher in people aged 40 years or older than in younger age groups. Age- and sex-adjusted prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with T1DM was 51.65% to 55.06% between 2009 and 2013.
Conclusion T1DM may be more common in Korean adults than previously believed. Metabolic syndrome may be a frequent finding in individuals with T1DM in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Increased risk of incident mental disorders in adults with new-onset type 1 diabetes diagnosed after the age of 19: A nationwide cohort study
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, So Hyun Cho, Rosa Oh, Ji Yoon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism.2024; 50(1): 101505. CrossRef - Incidence and trends of type 1 diabetes before and after 2000 in the Western Pacific Region: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Du Wang, Xiaoli Hou, Juan Huang, Jianjing Sun, Takashi Kadowaki, Moon-Kyu Lee, Alicia J. Jenkins, Linong Ji
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 207: 111055. CrossRef - The emergence of obesity in type 1 diabetes
Martin T. W. Kueh, Nicholas W. S. Chew, Ebaa Al-Ozairi, Carel W. le Roux
International Journal of Obesity.2024; 48(3): 289. CrossRef - Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Risk Factors Influence on Microvascular Complications in Patients With Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Asad Riaz, Shoaib Asghar, Salman Shahid, Haider Tanvir, Muhammad Hamza Ejaz, Mamuna Akram
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Depression according to Cumulative Exposure to a Low-Household Income Status in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population- Based Study
So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Kyu-na Lee, Bongsung Kim, So Hyun Cho, So Yoon Kwon, Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Kyungdo Han, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 290. CrossRef - Comparison of Insulin-Treated Patients with Ambiguous Diabetes Type with Definite Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Subjects: A Clinical Perspective
Insa Laspe, Juris J. Meier, Michael A. Nauck
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 140. CrossRef - Clinical and biochemical profile of childhood–adolescent-onset type 1 diabetes and adult-onset type 1 diabetes among Asian Indians
Viswanathan Mohan, Ganesan Uma Sankari, Anandakumar Amutha, Ranjit Mohan Anjana, Saravanan Jeba Rani, Ranjit Unnikrishnan, Ulagamathesan Venkatesan, Coimbatore Subramanian Shanthi Rani
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(4): 579. CrossRef - Subtypes of type 2 diabetes and their association with outcomes in Korean adults - A cluster analysis of community-based prospective cohort
You-Cheol Hwang, Hong-Yup Ahn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung
Metabolism.2023; 141: 155514. CrossRef - Insulin Fact Sheet in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Trends of Antidiabetic Medication Use in Insulin Users with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: 2002 to 2019
Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Bong-Sung Kim, Kyung-Do Han, So Yoon Kwon, So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 211. CrossRef - Insulin resistance is more frequent in type 1 diabetes patients with long disease duration
Yuting Xie, Mei Shi, Xiaolin Ji, Fansu Huang, Li Fan, Xia Li, Zhiguang Zhou
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-term Effectiveness of the National Diabetes Quality Assessment Program in South Korea
Ji Hye Huh, Serim Kwon, Gui Ok Kim, Bo Yeon Kim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes Care.2023; 46(9): 1700. CrossRef - Low Household Income Status and Death from Pneumonia in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Study
You-Bin Lee, So Hee Park, Kyu-na Lee, Bongsung Kim, So Yoon Kwon, Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Kyungdo Han, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 682. CrossRef - Impact of statin treatment on cardiovascular risk in patients with type 1 diabetes: a population-based cohort study
Joonsang Yoo, Jimin Jeon, Minyoul Baek, Sun Ok Song, Jinkwon Kim
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Microvascular Complications in Chinese Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Qianwen Huang, Daizhi Yang, Hongrong Deng, Hua Liang, Xueying Zheng, Jinhua Yan, Wen Xu, Xiangwen Liu, Bin Yao, Sihui Luo, Jianping Weng
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 93. CrossRef - The Incidence of Adult-Onset Type 1 Diabetes: A Systematic Review From 32 Countries and Regions
Jessica L. Harding, Pandora L. Wander, Xinge Zhang, Xia Li, Suvi Karuranga, Hongzhi Chen, Hong Sun, Yuting Xie, Richard A. Oram, Dianna J. Magliano, Zhiguang Zhou, Alicia J. Jenkins, Ronald C.W. Ma
Diabetes Care.2022; 45(4): 994. CrossRef - Age at Diagnosis and the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Jong Ha Baek, Woo Je Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Soo Kyoung Kim, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(1): 46. CrossRef - Genomic ancestry and metabolic syndrome in individuals with type 1 diabetes from an admixed population: a multicentre, cross‐sectional study in Brazil
B. S. V. Barros, D. C. Santos, L. G. N. Melo, M. H. Pizarro, L. H. Muniz, D. A. Silva, L. C. Porto, M. B. Gomes
Diabetic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Interplay Between Diet and the Epigenome in the Pathogenesis of Type-1 Diabetes
Amira Kohil, Maha Al-Asmakh, Mashael Al-Shafai, Annalisa Terranegra
Frontiers in Nutrition.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of early mortality and cardiovascular disease according to the presence of recently diagnosed diabetes and requirement for insulin treatment: A nationwide study
You‐Bin Lee, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Min Sun Choi, Jiyun Park, Minyoung Kim, Sang‐Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2021; 12(10): 1855. CrossRef - Age at Diagnosis and the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:46-54)
Ye Seul Yang, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 277. CrossRef - Comparison of fracture risk between type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a comprehensive real-world data
J. Ha, C. Jeong, K.-D. Han, Y. Lim, M.K. Kim, H.-S. Kwon, K.-H. Song, M.I. Kang, K.-H. Baek
Osteoporosis International.2021; 32(12): 2543. CrossRef - Early mortality and cardiovascular disease, varied association with body mass index and its changes in insulin-treated diabetes: a nationwide study
You-Bin Lee, Bongsung Kim, Jiyun Park, Minyoung Kim, Min Sun Choi, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Kyungdo Han, Jae Hyeon Kim
International Journal of Obesity.2021; 45(11): 2482. CrossRef - Young-onset type 2 diabetes in South Korea: a review of the current status and unmet need
Ye Seul Yang, Kyungdo Han, Tae Seo Sohn, Nam Hoon Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2021; 36(5): 1049. CrossRef - Positive association between the ratio of triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and diabetes incidence in Korean adults
Joungyoun Kim, Sang-Jun Shin, Ye-Seul Kim, Hee-Taik Kang
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Mortality and causes of death in a population with blindness in Korea: A longitudinal follow-up study using a national sample cohort
Hyo Geun Choi, Min Joung Lee, Sang-Mok Lee
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Hospitalization for heart failure incidence according to the transition in metabolic health and obesity status: a nationwide population-based study
You-Bin Lee, Da Hye Kim, Seon Mee Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Yong Gyu Park, Kyungdo Han, Hye Jin Yoo
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Adults
Hye Ryoung Yun
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(3): 156. CrossRef - New Insulin Pumps and Open Source Artificial Pancreas System in Korea
Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(4): 197. CrossRef - Risk of early mortality and cardiovascular disease in type 1 diabetes: a comparison with type 2 diabetes, a nationwide study
You-Bin Lee, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Seung-Eun Lee, Ji Eun Jun, Jiyeon Ahn, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of end‐stage renal disease from chronic kidney disease defined by decreased glomerular filtration rate in type 1 diabetes: A comparison with type 2 diabetes and the effect of metabolic syndrome
You‐Bin Lee, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Ji Eun Jun, Seung‐Eun Lee, Jiyeon Ahn, Gyuri Kim, Sang‐Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Increased risk of incident mental disorders in adults with new-onset type 1 diabetes diagnosed after the age of 19: A nationwide cohort study

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





